1. Superannuation
Superannuation in Australia refers to a system of compulsory retirement savings that are designed to provide income to individuals in retirement. Under this system, employers are required to make regular contributions to a superannuation fund on behalf of their employees, which is invested on their behalf to grow over time.
The superannuation system was introduced in Australia in 1992 as part of a package of economic reforms aimed at promoting individual responsibility for retirement savings and reducing reliance on government-provided pensions. The system has since become a central feature of the Australian retirement income system, with around 80% of the population having a superannuation account.
Employers in Australia are required by law to contribute at least 10% of an employee's earnings to a superannuation fund. This is known as the Superannuation Guarantee and is designed to ensure that individuals can accumulate sufficient savings to support themselves in retirement. Self-employed individuals are also required to make regular contributions to their superannuation.

2. Unfair dismissal
Unfair dismissal in Australia refers to the termination of an employee's employment by their employer in a manner that is considered unjust or unreasonable. The Fair Work Act 2009 outlines the circumstances in which an employee can make an unfair dismissal claim, such as when their dismissal was harsh, unjust, or unreasonable, or when it was not a genuine redundancy. The Act also provides protections against discriminatory dismissals based on factors such as race, gender, religion, or political affiliation. Employees who believe they have been unfairly dismissed may be able to pursue legal action to seek compensation or reinstatement to their former position.
3. Redundancy
Redundancy is a common occurrence in the Australian workforce, particularly in industries that are subject to rapid change or restructuring. Employers may make employees redundant for a variety of reasons, such as changes to the company's business strategy, a decline in demand for the company's products or services, or technological advancements that make certain roles redundant.
While redundancy can be a difficult experience for employees, it is important to note that employers are required to follow certain procedures when making employees redundant. This includes providing employees with notice of the redundancy, consulting with them about the proposed redundancy, and offering them the opportunity to apply for alternative positions within the company where possible. In addition, eligible employees are entitled to receive redundancy pay, which is designed to provide financial assistance while they look for alternative employment.
4. Jobactive
Jobactive is an employment services program in Australia that provides job seekers with assistance in finding and maintaining employment. The program is designed to support job seekers with various levels of employment barriers, including those who are long-term unemployed, have a disability or mental health condition, or are facing other personal or financial challenges. Jobactive providers work with job seekers to develop personalized employment plans, provide training and upskilling opportunities, and connect them with potential employers. Employers can also engage with jobactive providers to access a pool of job-ready candidates and receive support with recruitment and training. The program is funded by the Australian government and is part of a broader suite of employment services aimed at supporting Australians to find and maintain employment.

5. Enterprise bargaining
Enterprise bargaining in Australia is a process in which employers and employees negotiate terms and conditions of employment at the enterprise level. This process allows for the development of collective agreements that reflect the specific needs and circumstances of individual workplaces, while also providing a framework for minimum standards of employment. Enterprise bargaining agreements typically cover issues such as wages, working hours, leave entitlements, and other conditions of employment. The Fair Work Act 2009 sets out the requirements and guidelines for enterprise bargaining in Australia, including rules around bargaining periods, voting procedures, and dispute resolution mechanisms. An enterprise bargaining process is an important tool for ensuring that employers and employees are able to negotiate mutually beneficial agreements that support workplace productivity and provide fair and reasonable working conditions.
6. Overtime
Overtime in Australia refers to any hours worked by an employee that exceed their normal working hours. Under the Fair Work Act 2009, employees are entitled to receive additional pay for overtime work, which is typically calculated at a rate of time-and-a-half or double-time, depending on the applicable award or agreement. Overtime rates may also be prescribed by an employment contract or collective agreement. Employers are generally required to provide reasonable notice to employees before requiring them to work overtime unless there are exceptional circumstances. Employees may also have the right to refuse to work overtime in certain situations, such as if it would result in them working unreasonable hours or if they have caring responsibilities. Overtime is an important issue in Australian workplaces, as it can impact the health and safety, work-life balance, and financial well-being of employees.
7. Parental leave
Parental leave is a period of time that employees are entitled to take off work when they have a new child, such as through childbirth, adoption, or fostering. Employees are entitled to unpaid parental leave for up to 12 months, with some additional entitlements for primary carers.
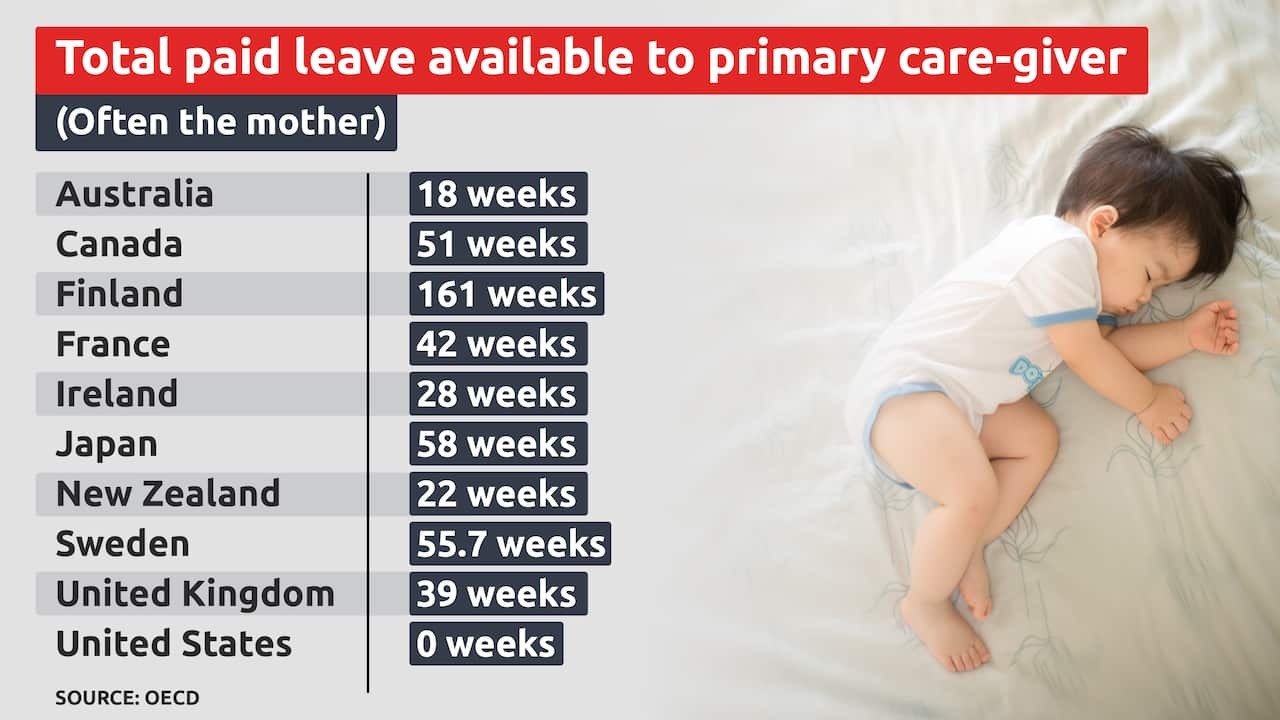
8. Sick leave
Sick leave is a form of paid leave that employees are entitled to take when they are unable to work due to illness or injury. Employees are entitled to 10 days of sick leave per year, which accumulates over time.
9. National Minimum Wage
The National Minimum Wage is the minimum amount that employers are legally required to pay their employees per hour of work. From 1 July 2022, the national minimum wage is $21.38 per hour or $812.60 per 38-hour week (before tax). Casual employees covered by the national minimum wage also get at least a 25% casual loading.

10. Casual loading
Casual loading refers to the additional pay rate that casual employees are entitled to, usually around 25% higher than the pay rate for permanent employees, to compensate for the lack of job security and other entitlements that permanent employees receive.
11. Work Health and Safety(WHS)
Work Health and Safety (WHS) refers to the laws, policies, and practices in place to ensure the health, safety, and welfare of workers and others in the workplace. Employers have a duty of care to provide a safe and healthy work environment, and employees have a responsibility to follow the WHS policies and procedures.
12. Fair Work Act
The Fair Work Act is the primary legislation that governs employment relationships in Australia. It sets out the minimum standards for employment, such as pay rates, working hours, and leave entitlements, as well as the rights and obligations of employers and employees.
13. Award
An award is a legal document that sets out the minimum pay rates and working conditions for employees in a particular industry or occupation. Awards are created by the Fair Work Commission and are legally binding on employers and employees in that industry or occupation.
14. Unions
Unions are organizations that represent the interests of workers in a particular industry or occupation. Unions advocate for better pay rates and working conditions, provide support and advice to their members and negotiate with employers on behalf of their members.
#labor#Parental leave#Superannuation##WHS#unions#Award#Redundancy
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.