English is a fascinating language, but it can be perplexing due to the presence of words that sound alike or have similar spellings, yet possess different meanings. These confusing words often lead to language misunderstandings and miscommunications. In this article, we will explore some commonly confused words in English, providing their meanings and offering example sentences to help you navigate these linguistic hurdles and communicate more effectively.
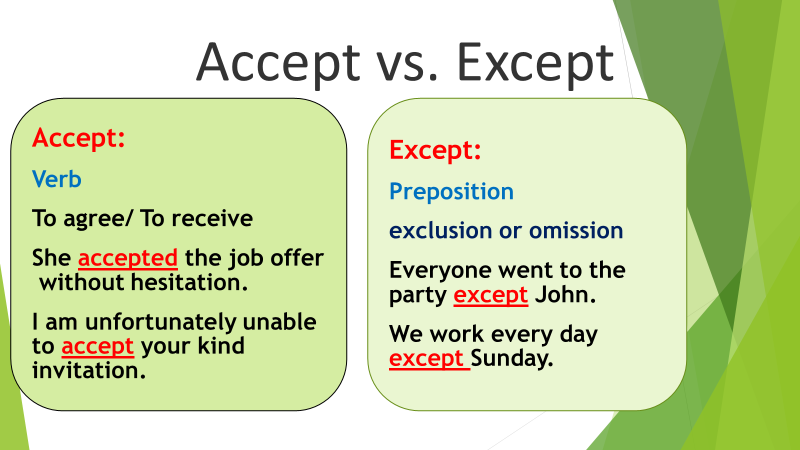
1. Accept vs. Except:
Meaning: "Accept" is a verb that denotes the action of receiving or agreeing to something.
Example: "She accepted the job offer without hesitation."
Meaning: "Except" is a preposition that signifies exclusion or omission.
Example: "Everyone went to the party except John."
2. Affect vs. Effect:
Meaning: "Affect" is commonly used as a verb and indicates the act of influencing or causing a change
Example: "The sudden loss affected her deeply."
Meaning: "Effect" is predominantly used as a noun and represents the result or consequence of something.
Example: "The new policy had a positive effect on the company's productivity."

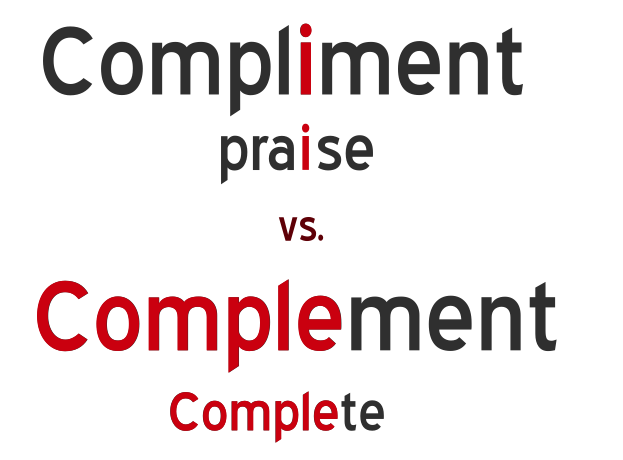
3. Complement vs. Compliment:
Meaning: "Complement" can be used as both a noun and a verb, referring to something that completes or enhances another thing.
Example: "The red wine perfectly complements the flavors of the dish."
Meaning: "Compliment" can function as both a noun and a verb, indicating an expression of admiration or praise.
Example: "She received a heartfelt compliment on her artistic skills."
4. Advise vs. Advice:
Meaning: "Advise" is a verb that conveys the act of offering guidance or recommendations. [
Example: "I advise you to consult a financial advisor."
Meaning: "Advice" is a noun that represents suggestions or recommendations given to someone.
Example: "She sought advice from her mentor before making a decision."

5. Lose vs. Loose:
Meaning: "Lose" is a verb that implies misplacing or being deprived of something.
Example: "Don't lose your keys; they are essential."
Meaning: "Loose" is an adjective that describes something not firmly fixed or tight.
Example: "Her hair fell in loose waves around her shoulders."

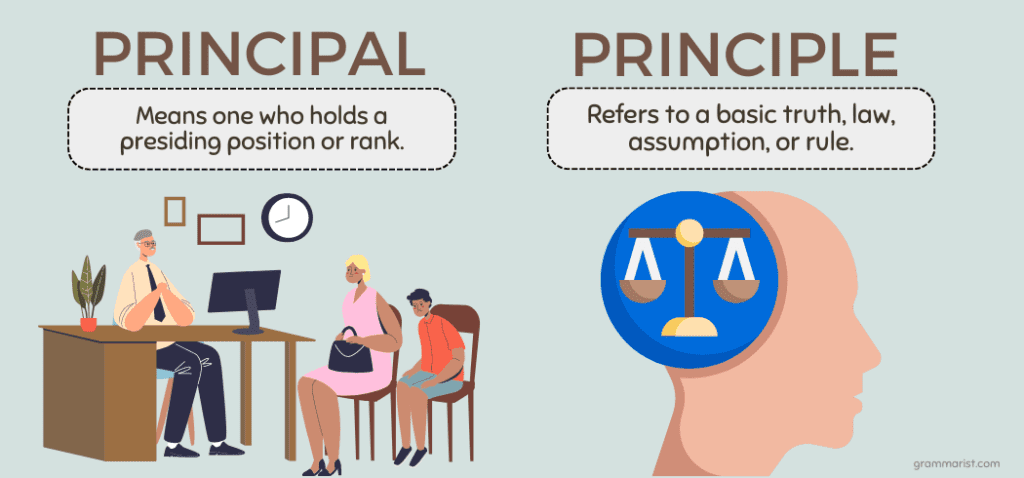
6. Principal vs. Principle: homophones /ˈprɪnsəpl/(English, American)
Meaning: "Principal" can have multiple meanings, such as the head of a school or an important person in an organization.
Example: "The principal of the school greeted the students every morning."
Meaning: "Principle" is a noun that signifies a fundamental truth or belief.
Example: "She firmly believes in the principles of equality and justice."
7. Stationary vs. Stationery: /ˈsteɪʃənri/(English), /ˈsteɪʃəneri/(American)
Meaning: "Stationary" is an adjective that describes something that is not moving or still.
Example: "The car remained stationary at the traffic light."
Meaning: "Stationery" is a noun that refers to writing materials, such as paper, pens, and envelopes.
Example: "She bought beautiful stationery for her correspondence."

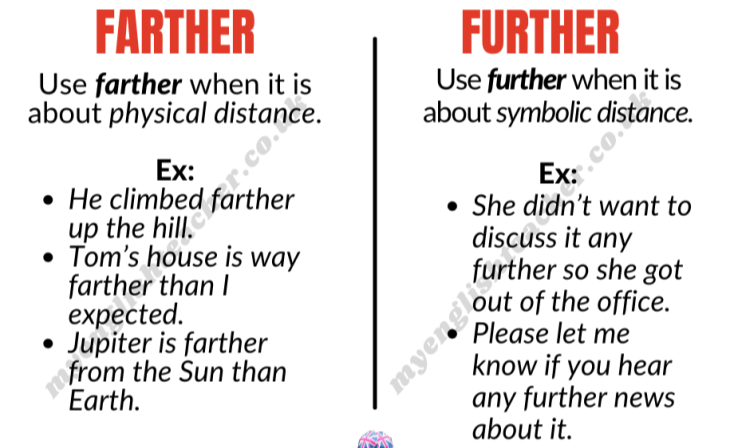
8. Farther vs. Further:
Meaning: "Farther" relates to physical distance and is used when referring to a measurable, tangible distance.
Example: "The shop is farther away than I anticipated."
Meaning: "Further" is more abstract and refers to a figurative or metaphorical distance.
Example: "Let's delve further into this topic."
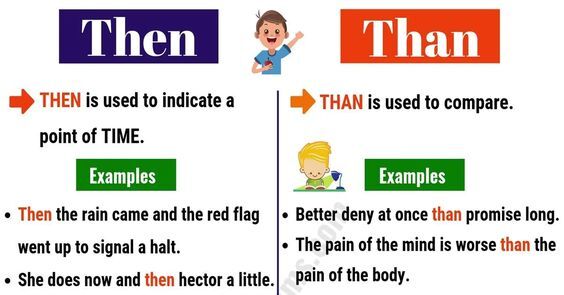
9. Than vs. Then:
Meaning: "Than" is used in making comparisons, indicating a difference or preference.
Example: "She is taller than her brother."
Meaning: "Then" relates to time and is used to show a sequence of events or a consequence.
Example: "Finish your homework, and then you can play."
10. Capital vs. Capitol:ˈhomophones /kæpɪtl/(English, American)
Meaning: "Capital" has multiple meanings, including the main city of a country or state, financial resources, or uppercase letters.
Example: "London is the capital of England."
Meaning: "Capitol" specifically refers to a building where a legislative body meets.
Example: "the California state capitol"

11. Desert vs. Dessert:
Meaning: "Desert" refers to a dry, arid region.
Example: "They explored the vast Sahara Desert."
Meaning: "Dessert" refers to a sweet treat eaten after a meal.
Example: "I ordered a delicious chocolate cake for dessert."

12. Breathe vs. Breath:
Meaning: "Breathe" is a verb that refers to the act of inhaling and exhaling air.
Example: "Take a deep breath and breathe slowly."
Meaning: "Breath" is a noun that represents a single inhalation or exhalation of air.
Example: "Her breath smelled like fresh mint."

Language learning is a continuous process, and I believe that I will be able to use English well if I continue to practice without fear of making mistakes.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.